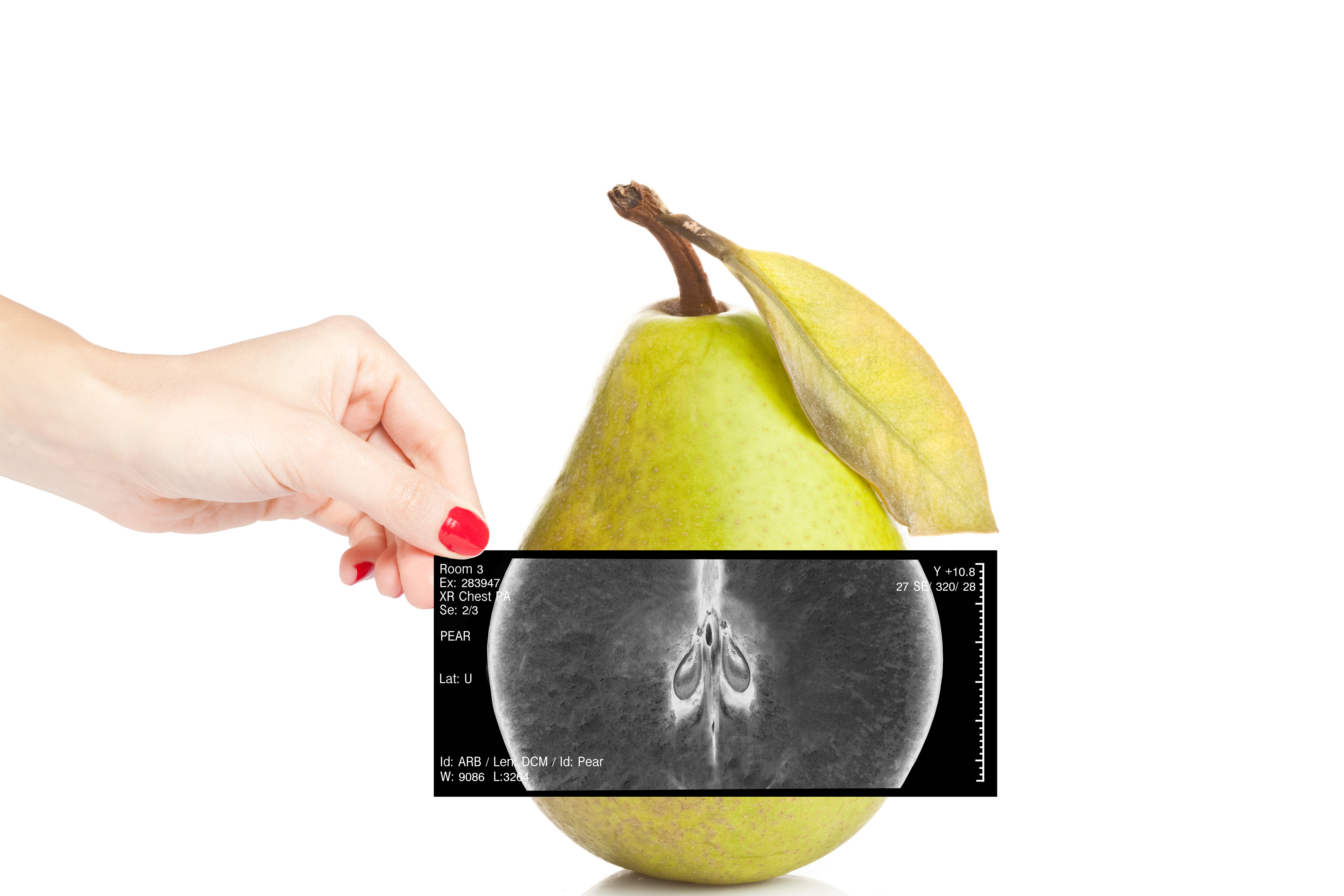
Follow HACCP plan
with X-ray Inspection
HACCP protects food brands
Today, HACCP is the most used and well-known food safety and quality control requirement that most food producers all over the world are following and not in vain:
food ingredients we consume have an impact on our physical wellbeing.
It is obvious that in food manufacturing plants, food is produced for the masses, and any safety or quality defect in any part of the food production can turn into a massive recall causing financial and reputational damages for food brands and health risks for consumers.
For example, allergens can have a huge risk for certain people. It’s the manufacturer’s responsibility to ensure contaminant-free production and that each ingredient is properly listed in the product labeling. If there is an identified contamination risk or mislabeling, food producers’ responsibility is to react quickly to prevent the products from causing harm to consumers. Usually, this means recalling the products that were identified as faulty or contaminated.
This applies to other health risks as well. Whereas peanuts can be almost a deadly ingredient for a nut-allergic person, other physical hazards are a safety risk for everyone, especially for the elderly or children who are not able to eat without assistance.
Avoid Recalls with X-Ray Inspection

The goal is to ensure food safety
FDA (U.S Food and Drug Administration) suggests that the importance of finding all health risks which might exist in the production, and the actions that are required to eliminate or reduce them, increases together with the complexity of the production.
HACCP is designed to address food safety through the analysis and control of hazards in the food supply chain, from production to distribution and consumption. It is a management system, which attempts to localize, evaluate, and control processes in production that can have an impact on safety and quality.
In HACCP, the goal is to ensure food safety by understanding all the potential hazards that are present in each part of the production. This happens with carefully designed production systems that minimize the related risks during each step and by establishing control points to places where a certain risk can be identified and eliminated and where the control can be applied.
With the HACCP plan and its correct implementation, food producers can agree that the processes in use are not causing any unexpected risks. It is a safety system that helps in preparing and controlling the whole production and identifying when and where risks could happen.
Even though HACCP is not the only food quality standard, it is the most common one that food producers all over the world are following.
Achieve food industry standardsThere are three types of hazards
There are biological, chemical, or physical agents that are likely to cause illness or injury if measures are not taken to reduce their occurrence in food production. Hence, a hazard is related to food safety. In order to produce safe food, make sure that these risks are taken into account in each part of designing the food production and food supply chain:
Biological hazards can be e.g., food-borne viruses, zoonoses (Salmonella, Campylobacter) and other
Chemical hazards are e.g., mycotoxins, dioxins, antibiotics, hormones, nitrates and other
Physical hazards are e.g., stone, glass, metal, plastic
They can be naturally occurring or intentionally/unintentionally added. For example, living organisms such as bacteria and molds in food can be naturally occurring, but still, cause illness if the health risk is not eliminated through proper actions, such as washing potatoes before cooking.
o Hazards can be introduced during or derive from the following:
- raw materials
- processing
- manufacturing practices
- packaging
- packaging material
- distribution
- consumption
Biological and chemical hazards are usually inspected on laboratories and risks of them are minimized, for example, by following legal rules of commonly agreed food production practices that suggest appropriate storaging conditions, temperatures for heating, animal nutrition etc. Physical hazards are a bit trickier to inspect or minimize from production as they are inside the food and usually cannot be seen or inspect by human eye without proper equipment. Also, the constant risk for foreign object contamination exists in almost every food production environment.
Read How Foreign Object Detection Works with X-Ray
Prerequisite programs as a foundation of HACCP
Conditions that protect food in each part of the production process must be ensured, but how? Different food production environments can be unique in nature but there are still some general aspects to consider in developing safe food production practices and equipment.
Prerequisite programs (PRP) provide the basic environmental and operating conditions that are necessary to produce safe food and they act as a foundation for HACCP implementation. According to FDA, this has traditionally been accomplished through the application of CGMPs (Current Good Manufacturing Practices) but now these conditions and practices are now considered to be prerequisite to the development and implementation of effective HACCP plans.
Many of these prerequisite programs are agreed by food authorities across the world and designed for parts of the food production process, e.g., facilities, suppliers, equipment, hygiene and cleaning, training, etc. They include suggestions and legal rules for actions/methods how to ensure safe food production in each part.
All prerequisite programs should be documented and regularly audited. Make sure you’re familiar with local regulations!
Monitoring the results of the current production processes and prerequisite programs is necessary to be able to control and identify risks and take corrective actions towards more safe food production, and HACCP is a great tool in this. For complex food production environments, PRP is not enough. Especially when it comes to foreign object contamination, following a HACCP plan correctly is a method to make sure safety is taken into account in each part of the complex food supply chain. With an X-ray system as one of your critical control points, you gain more value on top of the inspection of foreign objects.
Find out how MEKI X-ray Systems fits in almost any food production
